In 1956 a group of scientists, mathematicians and humanists met at Dartmouth College. Among them were Marvin Minsky, Claudius Shannon and John Nash – he of ‘The Beautiful Mind’ – gathered to speak. a completely new discipline. Those two words are everywhere, but at the time they sounded strange and utopian.
These two words mean nothing else artificial intelligence.
That name came across to John McCarthy, a young professor at that institution, who worked for a year to organize that cycle of meetings. Everyone who took part in that conference came out enthusiastically about the idea of creating artificial intelligence, even though they were coming face to face with a terrible reality: they were ahead of their time. The computing power of time has not allowed us to solve the big AI challenges.
Hello artificial neural networks
The training, however, was gradually progressing in several columns. One of them, the artificial neural networks (ANNs) is especially promising for one of the big problems at hand: model recognition.
This problem allowed, for example, to interpret images and for the machine to know what the image shows. For example, what a dog was a dog or a man was a man; Work in that field progressed erratically, but in 1982 something was done.
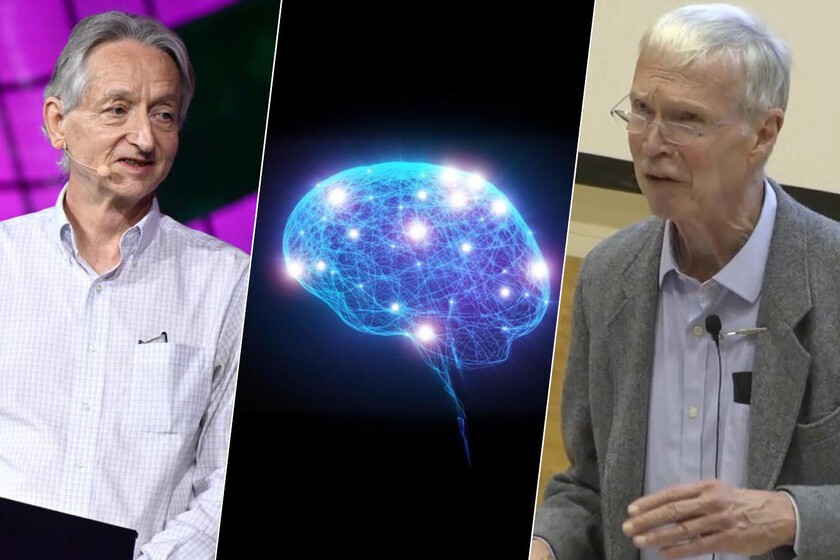
this year John Hopfieldtheoretical physicist, born in 1933, and the son of two theoretical physicists – published work on an associative memory model based on a recurrent neural network. The concepts he discussed were closely connected to the field of physics, although applied to the field of computing – specifically to the description of magnetic materials, and Hopfield was very clear about that.
His idea was unique and allowed the initial system with a faulty model, for example, a misspelt word, to be “attracted to the energy of the “lowest” node in the neural network, in the correction of the system that the effect of the word was intact.
The idea ended up being worked on by Hopfield and David Tank in 1986. In that system they proposed all problems are solved inspired by how physical systems behave over time
In the “analog model”, as they called it, instead of numbers (zeros and ones) and working computers, they used a system that changed gently, gradually and continuously. They posed a network problem in which the connections between the different parts of the network had certain weights and led the system to achieve the optimal solution. According to the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences“Hopfeld founded the effort to understand the computational capabilities of neural networks.”
This is Hopfield’s work Geoffrey Hinton’s work is crucialwho worked between 1983 and 1985 with Terrence Sejnowski and other researchers to develop the stochastic (probabilistic) expansion model of Hopfield’s 1982 model.
It was a generative model.
In this it differed from Hopfeld’s model. Here Hinton focused on the distribution of statistical patterns, and not on individual patterns. Your Boltzmann machineand recurrent neural networks– They contained visible nodes that corresponded to patterns that needed to be “learned.” The system tries to learn how different solutions are good or bad when solving a problem, it does not focus on one exact solution.
In addition to visible nodes, the engine has hidden nodes, additions that allow the engine to capture more complex and varied relationships between those models. Hidden nodes also allow for the ability to model many possible understandings, not limited to the specific forms we show you. Or the same thing; He can generate things that I have not seen but they probably make sense.
From ANNs to ChatGPT
Both the Hopfield model and the Boltzmann machine allowed very interesting applications to be developed in the following years. Among others for review patterns in images, texts and clinical data. From that work, Yann LeCun (now the head of AI at Meta) and Yoshua Bengio envisioned convolutional neural networks (CNN), which were applied to curious things: several banking entities in the US used LeCun’s work to insert handwritten fingers into the middle of checks. 1990s


Hinton’s contribution did not end there. At the turn of the millennium, he worked out the changes of his project, which is called the restricted Boltzmann machine, which worked much faster and allowed working with very dense networks with several layers, which would lead to the establishment of a special characteristic of training; high learning or deep learning.
Extraordinary applications of ANNs have been achieved in many fields such as astrophysics or astronomy, but also in the field of computing. The Swedish Academy provides an example AlphaFold, the DeepMind projectand this type of models with artificial networks is neutral They are used for example in chatbots like ChatGPT, Gemini or Claude.
Therefore, the work of the two Nobel Prize winners in physics was fundamental to the development of this entire field, and although both before, during and after Hopfield and Hinton, many more people worked to develop it, their work is the “fathers of AI. and has also been considered worthy of this prestigious award
Image | Collision Conf | Bhadeshia